Single Image Dehazing using a Multilayer Perceptron
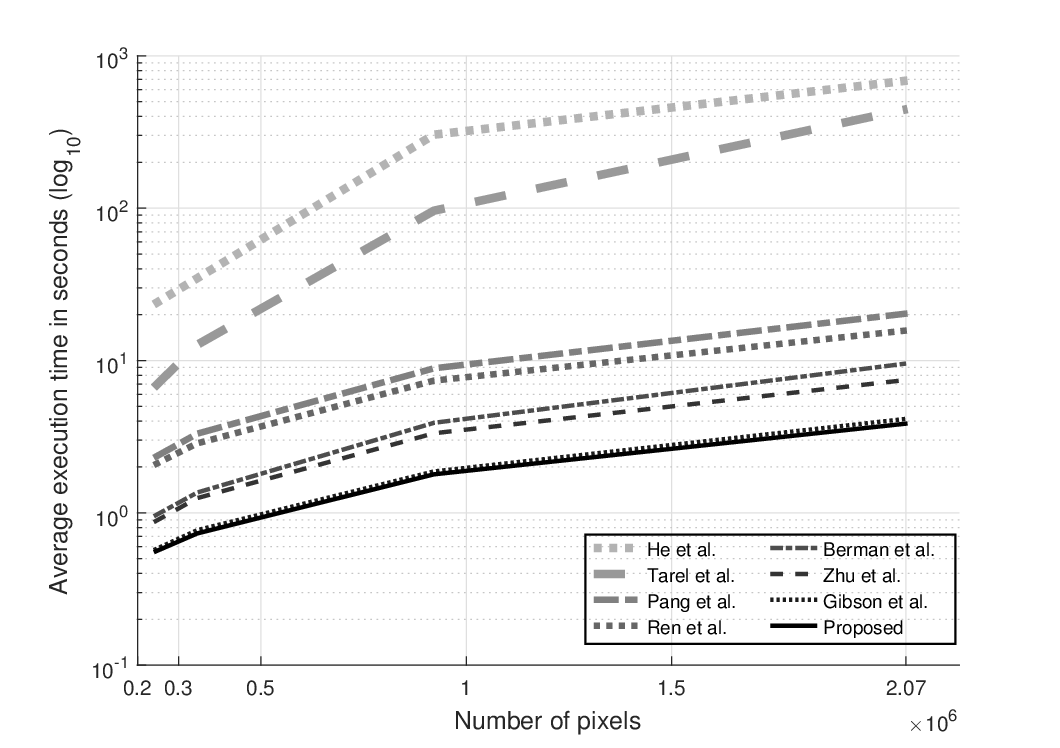
This paper presents a novel algorithm to improve images with hazing effects. Usually the dehazing methods based on the dark channel prior, make use of two different stages to compute the transmission map of the input image. The stages are the transmission map estimation and a transmission map refinement. However, the main disadvantage of these strategies is the trade-off between accurate restoration and computational time. The proposed method uses a Multilayer Perceptron to compute the transmission map directly from the minimum channel, and a contrast stretching technique to improve the dynamic range of the restored image. The Multilayer Perceptron is trained in terms of Mean Squared Error (MSE) using a training set of 80 images. To evaluate the restoration quality, the metrics of Mean Absolute Error (MAE), and the Structural Similarity (SSIM) index are used. The experimental results have proven that the proposed method achieves superior performance in terms of restoration quality (MAE = 27.28, SSIM index = 0.84) compared with seven state-of-the-art dehazing methods. In addition, based on the average computational time achieved by the proposed method (0.52 seconds using a test set of 40 images), it can be highly suitable for real-time applications.
Authors:
Sebastian Salazar-Colores, Ivan Cruz-Aceves*, and Juan Ramos-ArreguinResearch paper published by Journal of Electronic Imaging, SPIE (March,2018)
Journal of Electronic Imaging, 27(4), 043022 (2018), https://doi.org/10.1117/1.JEI.27.4.043022
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)



.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)