Improving Automatic Coronary Stenosis Classification using a Hybrid Metaheuristic with Diversity Control
In the present work, an improved Hybrid Metaheuristic with a Diversity Control is proposed. The method is focused on finding an optimal feature subset, which is able to improve the performance in the automatic classification of coronary stenosis cases. Compared with traditional evolutionary computing approaches, which considers only the best individuals of a population, the proposed strategy considers the worst individuals under certain conditions. By applying the diversity control, the search space which involves a high-dimensional complexity, is explored widely. In consequence, the feature selection frequencies trends to be uniform, decreasing the probability of premature convergent results and local-optima solutions. The experiments involved the formation of a dataset, consisting of $608$ instances and $473$ features, from an image database of X-ray coronary angiographies. Using the proposed strategy, it was achieved a classification rate of $0.92$ and $0.85$ in terms of the Accuracy and the Jaccard Coefficient metrics, respectively, using only $16$ of the $473$ initial features. In addition, the average time required for the classification of a single instance was $0.0003$ seconds. Based on the achieved results, the found feature subset is adequate to be used in clinical practice in support decision information systems.
The present ground-truth database of positive and negative images of coronary stenosis is available to the scientific community for research and comparison purposes.
Authors:
Miguel A. Gil-Rios, Ivan Cruz-Aceves*, Arturo Hernández-Aguirre, Martha A. Hernández-González, and Sergio Solorio-MezaResearch paper (reference): Gil-Rios, Miguel-Angel, Ivan Cruz-Aceves, Arturo Hernandez-Aguirre, Martha-Alicia Hernandez-Gonzalez, and Sergio-Eduardo Solorio-Meza. 2024. "Improving Automatic Coronary Stenosis Classification Using a Hybrid Metaheuristic with Diversity Control" Diagnostics 14, no. 21: 2372. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14212372
Experimental results
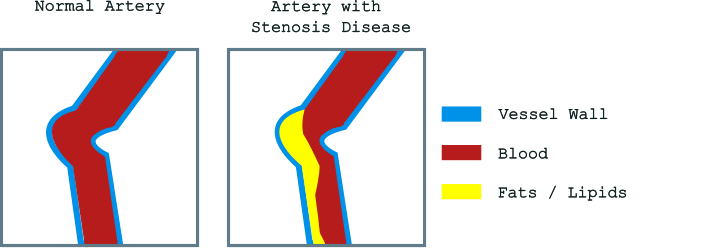
Schematic representation of a normal artery (left) and an obstructed artery by the accumulation of fats/lipids (right).
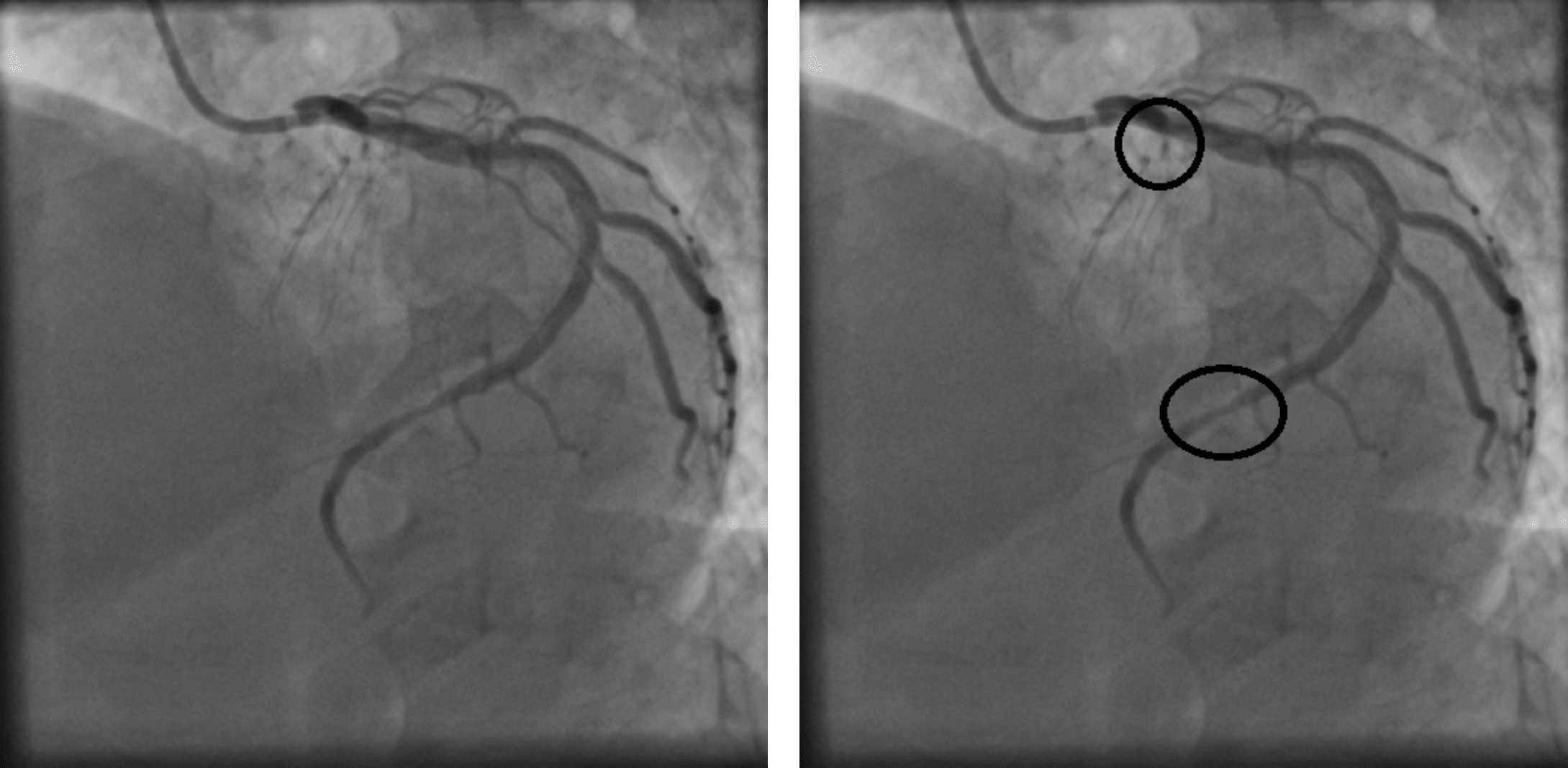
A coronary angiography (left) with their respective stenosis areas labeled by the cardiology specialist (right).
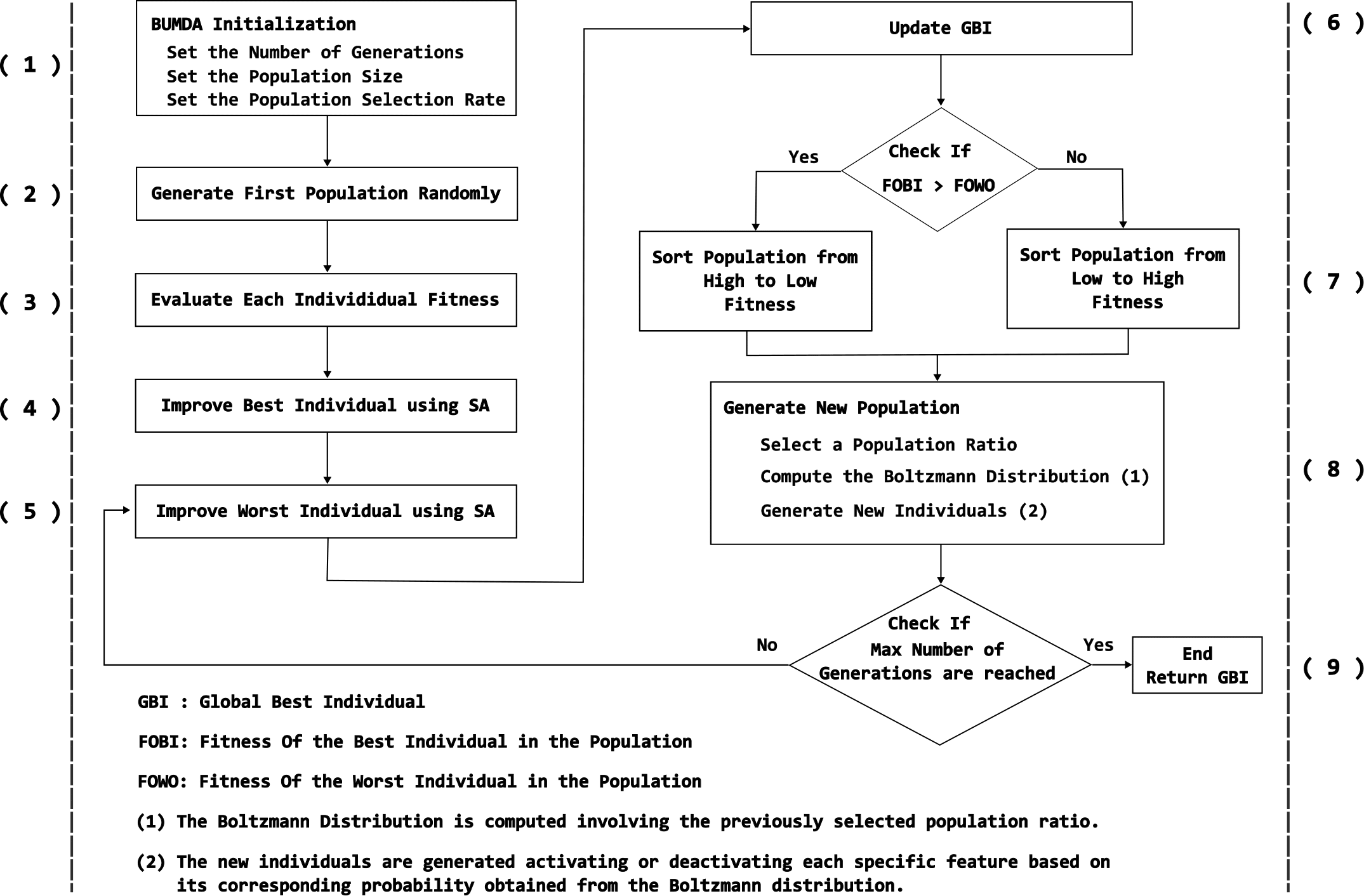
Overall process of the hybrid metaheuristic based on BUMDA and SA with diversity control, for automatic feature selection.
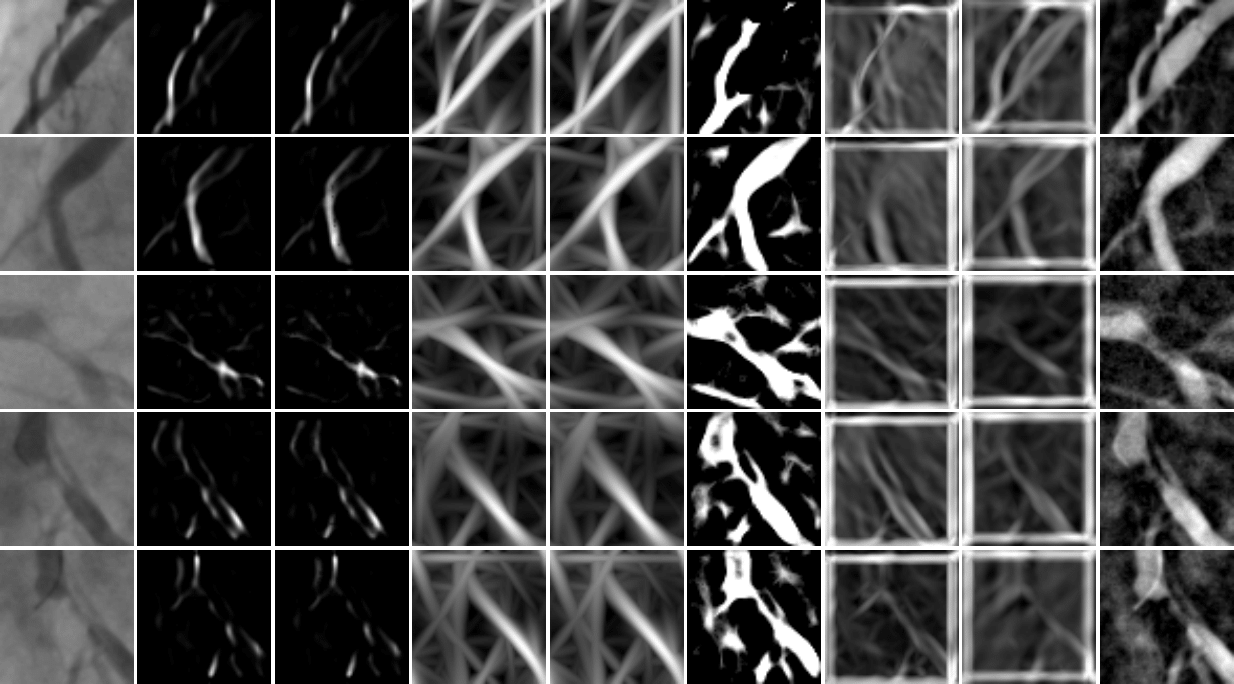
Vessel enhancement responses from $8$ distinct filtering methods. Each row corresponds to a coronary patch. In columns $1$ to $9$, are described $8$ distinct vessel enhancement methods response as follows: Original image, Frangi filter, Salem filter, Single-Scale Gabor filter, Multi-Scale Gabor filter, Multi-Scale filter, Single-Scale Gaussian-Matched Filter, Multi-Scale Gaussian-Matched Filter and, the Top-Hat operator.
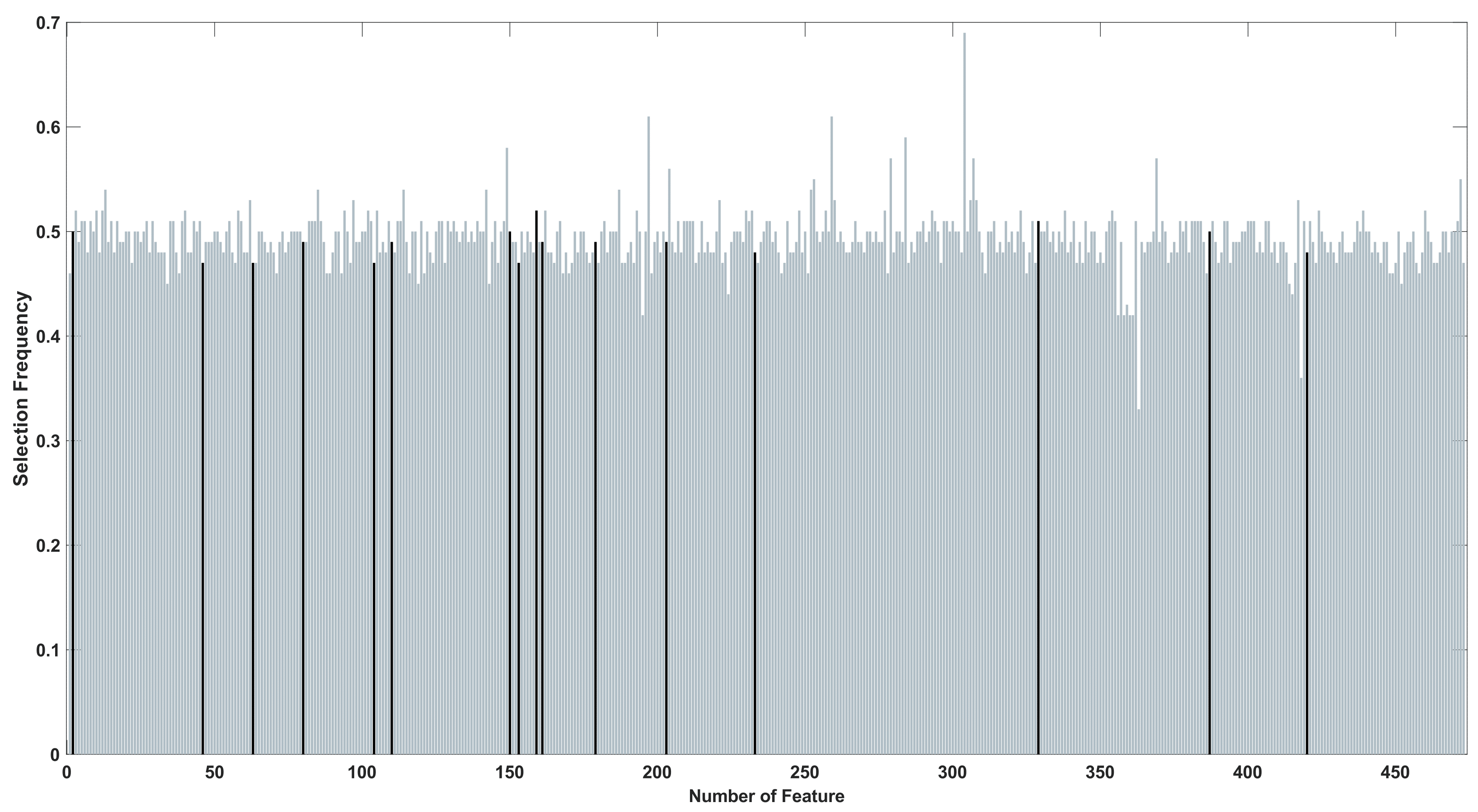
Feature selection frequencies involving the BUMDA and the SA with a diversity control, which conforms the proposed method. The selected $16$ features are remarked.
Downloads
Database of 608 Positive and Negative Coronary Stenosis images (pgm format)
Downloads
Dataset (csv) of 473 Features computed from the 608 Positive and Negative Coronary Stenosis images